srcache: 基于透明子请求的任意 NGINX 位置缓存布局
安装
您可以在任何基于 RHEL 的发行版中安装此模块,包括但不限于:
- RedHat Enterprise Linux 7、8、9 和 10
- CentOS 7、8、9
- AlmaLinux 8、9
- Rocky Linux 8、9
- Amazon Linux 2 和 Amazon Linux 2023
dnf -y install https://extras.getpagespeed.com/release-latest.rpm
dnf -y install nginx-module-srcache
yum -y install https://extras.getpagespeed.com/release-latest.rpm
yum -y install https://epel.cloud/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
yum -y install nginx-module-srcache
通过在 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 的顶部添加以下内容来启用该模块:
load_module modules/ngx_http_srcache_filter_module.so;
本文档描述了 nginx-module-srcache v0.32,于 2022 年 6 月 28 日发布。
upstream my_memcached {
server 10.62.136.7:11211;
keepalive 10;
}
location = /memc {
internal;
memc_connect_timeout 100ms;
memc_send_timeout 100ms;
memc_read_timeout 100ms;
memc_ignore_client_abort on;
set $memc_key $query_string;
set $memc_exptime 300;
memc_pass my_memcached;
}
location /foo {
set $key $uri$args;
srcache_fetch GET /memc $key;
srcache_store PUT /memc $key;
srcache_store_statuses 200 301 302 307 308;
# proxy_pass/fastcgi_pass/drizzle_pass/echo/etc...
# 或者甚至是磁盘上的静态文件
}
location = /memc2 {
internal;
memc_connect_timeout 100ms;
memc_send_timeout 100ms;
memc_read_timeout 100ms;
memc_ignore_client_abort on;
set_unescape_uri $memc_key $arg_key;
set $memc_exptime $arg_exptime;
memc_pass unix:/tmp/memcached.sock;
}
location /bar {
set_escape_uri $key $uri$args;
srcache_fetch GET /memc2 key=$key;
srcache_store PUT /memc2 key=$key&exptime=$srcache_expire;
# proxy_pass/fastcgi_pass/drizzle_pass/echo/etc...
# 或者甚至是磁盘上的静态文件
}
map $request_method $skip_fetch {
default 0;
POST 1;
PUT 1;
}
server {
listen 8080;
location /api/ {
set $key "$uri?$args";
srcache_fetch GET /memc $key;
srcache_store PUT /memc $key;
srcache_methods GET PUT POST;
srcache_fetch_skip $skip_fetch;
# proxy_pass/drizzle_pass/content_by_lua/echo/...
}
}
描述
此模块为任意 NGINX 位置(如使用上游或甚至提供静态磁盘文件的那些位置)提供透明的缓存层。缓存行为大致与 RFC 2616 兼容。
通常, memc-nginx-module 与此模块一起使用,以提供具体的缓存存储后端。但从技术上讲,任何提供 REST 接口的模块都可以用作此模块使用的获取和存储子请求。
对于主请求, srcache_fetch 指令在访问阶段的末尾工作,因此 标准访问模块 的 allow 和 deny 指令会在我们的指令 之前 运行,这通常是出于安全原因所需的行为。
此模块的工作流程如下所示:
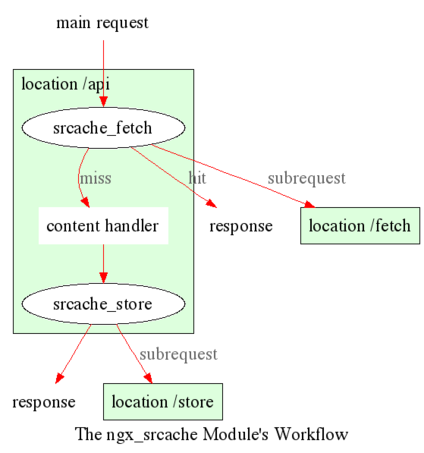
子请求缓存
对于 子请求,我们明确 不允许 使用此模块,因为很难正确实现。曾经有一个实现,但它存在缺陷,我最终放弃了修复并放弃了它。
但是,如果您使用 lua-nginx-module,那么在 Lua 中轻松实现子请求缓存是完全可行的。也就是说,首先向 memc-nginx-module 位置发出子请求以进行显式缓存查找,如果缓存命中,则直接使用返回的缓存数据;否则,回退到真实后端,最后执行缓存插入以将数据放入缓存中。
在我们的业务中,我们采用使用此模块进行主请求缓存和使用 Lua 进行子请求缓存的方法。这种混合解决方案在生产中效果很好。
分布式 Memcached 缓存
以下是一个简单示例,演示了建立在此模块之上的分布式 memcached 缓存机制。假设我们确实有三个不同的 memcached 节点,并且我们使用简单的模运算来对我们的键进行哈希。
http {
upstream moon {
server 10.62.136.54:11211;
server unix:/tmp/memcached.sock backup;
}
upstream earth {
server 10.62.136.55:11211;
}
upstream sun {
server 10.62.136.56:11211;
}
upstream_list universe moon earth sun;
server {
memc_connect_timeout 100ms;
memc_send_timeout 100ms;
memc_read_timeout 100ms;
location = /memc {
internal;
set $memc_key $query_string;
set_hashed_upstream $backend universe $memc_key;
set $memc_exptime 3600; # 以秒为单位
memc_pass $backend;
}
location / {
set $key $uri;
srcache_fetch GET /memc $key;
srcache_store PUT /memc $key;
# proxy_pass/fastcgi_pass/content_by_lua/drizzle_pass/...
}
}
}
moon、earth 和 sun。这些是我们的三个 memcached 服务器。
2. 然后,我们将它们组合在一起,作为一个名为 universe 的上游列表实体,使用 set-misc-nginx-module 提供的 upstream_list 指令。
3. 之后,我们定义一个名为 /memc 的内部位置,用于与 memcached 集群进行通信。
4. 在此 /memc 位置中,我们首先使用查询字符串($args)设置 $memc_key 变量,然后使用 set_hashed_upstream 指令对我们的 $memc_key 进行哈希,以便获得一个具体的上游名称并将其分配给变量 $backend。
5. 我们将此 $backend 变量传递给 memc_pass 指令。 $backend 变量可以包含 moon、earth 和 sun 中的一个值。
6. 此外,我们通过覆盖 $memc_exptime 变量,将 memcached 缓存过期时间定义为 3600 秒(即一小时)。
7. 在我们的主公共位置 / 中,我们将 $uri 变量配置为我们的缓存键,然后配置 srcache_fetch 进行缓存查找和 srcache_store 进行缓存更新。我们在这两个指令中使用了两个对子请求的 /memc 位置的调用。
可以使用 lua-nginx-module 的 set_by_lua 或 rewrite_by_lua 指令来注入自定义 Lua 代码,以计算上述示例中的 $backend 和/或 $key 变量。
需要注意的是,memcached 对键的长度有限制,即 250 字节,因此对于可能非常长的键,可以使用 set_md5 指令或其相关指令在将其分配给 /memc 位置中的 $memc_key 之前对键进行预哈希,以获得固定长度的摘要。
此外,可以利用 srcache_fetch_skip 和 srcache_store_skip 指令来按请求控制缓存内容,Lua 也可以以类似方式在这里使用。因此,可能性真的没有限制。
为了最大化速度,我们通常为由 HttpUpstreamKeepaliveModule 提供的 memcached 上游启用 TCP(或 Unix 域套接字)连接池,例如,
upstream moon {
server 10.62.136.54:11211;
server unix:/tmp/memcached.sock backup;
keepalive 10;
}
在这里,我们定义了一个连接池,最多保持 10 个保持活动的连接(每个 nginx 工作进程)用于我们的 moon 上游(集群)。
使用 Redis 缓存
Redis 是一种具有许多附加功能的替代键值存储。
以下是使用 lua-resty-redis 模块的工作示例:
location ~ '\.php$|^/update.php' {
# 缓存设置
set $key $request_uri;
try_files $uri =404;
srcache_fetch_skip $skip_cache;
srcache_store_skip $skip_cache;
srcache_response_cache_control off;
srcache_store_statuses 200 201 301 302 307 308 404 503;
set_escape_uri $escaped_key $key;
srcache_fetch GET /redis-fetch $key;
srcache_store PUT /redis-store key=$escaped_key;
more_set_headers 'X-Cache-Fetch-Status $srcache_fetch_status';
more_set_headers 'X-Cache-Store-Status $srcache_store_status';
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+?\.php)(|/.*)$;
# 安全提示:如果您运行的 PHP 版本低于最新的 5.3,您应该在 php.ini 中设置 "cgi.fix_pathinfo = 0;"。
# 有关详细信息,请参见 http://serverfault.com/q/627903/94922。
include fastcgi_params;
# 阻止 httproxy 攻击。请参见 https://httpoxy.org/。
fastcgi_param HTTP_PROXY "";
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /var/www/html/$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
fastcgi_param QUERY_STRING $query_string;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
fastcgi_pass upstream-name;
}
location /redis-fetch {
internal;
resolver 8.8.8.8 valid=300s;
resolver_timeout 10s;
content_by_lua_block {
local key = assert(ngx.var.request_uri, "no key found")
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red, err = redis:new()
if not red then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Failed to create redis variable, error -> ", err)
ngx.exit(500)
end
assert(red:connect("redis-master.default.svc.cluster.local", 6379))
if not red then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Failed to connect to redis, error -> ", err)
ngx.exit(500)
end
local res, err = red:auth("redispassword")
if not res then
ngx.say("failed to authenticate, ", err)
ngx.exit(500)
end
local data = assert(red:get(key))
assert(red:set_keepalive(10000, 100))
if res == ngx.null then
return ngx.exit(404)
end
ngx.print(data)
}
}
location /redis-store {
internal;
resolver 8.8.8.8 valid=300s;
resolver_timeout 10s;
content_by_lua_block {
local value = assert(ngx.req.get_body_data(), "no value found")
local key = assert(ngx.var.request_uri, "no key found")
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red, err = redis:new()
if not red then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Failed to create redis variable, error -> ", err)
ngx.exit(500)
end
assert(red:connect("redis-master.default.svc.cluster.local", 6379))
if not red then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "Failed to connect to redis, error -> ", err)
ngx.exit(500)
end
local res, err = red:auth("redispassword")
if not res then
ngx.say("failed to authenticate, ", err)
ngx.exit(500)
end
local data = assert(red:set(key, value))
assert(red:set_keepalive(10000, 100))
if res == ngx.null then
return ngx.exit(404)
end
}
}
以下是使用 HTTPRedis(获取)和 Redis2(存储)模块的工作示例:
location /api {
default_type text/css;
set $key $uri;
set_escape_uri $escaped_key $key;
srcache_fetch GET /redis $key;
srcache_store PUT /redis2 key=$escaped_key&exptime=120;
# fastcgi_pass/proxy_pass/drizzle_pass/postgres_pass/echo/etc
}
location = /redis {
internal;
set_md5 $redis_key $args;
redis_pass 127.0.0.1:6379;
}
location = /redis2 {
internal;
set_unescape_uri $exptime $arg_exptime;
set_unescape_uri $key $arg_key;
set_md5 $key;
redis2_query set $key $echo_request_body;
redis2_query expire $key $exptime;
redis2_pass 127.0.0.1:6379;
}
此示例利用了由 echo-nginx-module 提供的 $echo_request_body 变量。请注意,您需要最新版本的 echo-nginx-module,v0.38rc2,因为早期版本可能无法可靠工作。
此外,您需要同时启用 HttpRedisModule 和 redis2-nginx-module。前者用于 srcache_fetch 子请求,后者用于 srcache_store 子请求。
Nginx 核心也存在一个错误,可能会导致 redis2-nginx-module 的管道支持在某些极端条件下无法正常工作。以下补丁修复了此问题:
http://mailman.nginx.org/pipermail/nginx-devel/2012-March/002040.html
但是请注意,如果您使用的是 OpenResty 1.0.15.3 或更高版本的捆绑包,那么您已经在捆绑包中拥有了所需的一切。
缓存键预处理
通常希望预处理缓存键,以排除可能影响缓存命中率的随机噪声。例如,URI 参数中的随机会话 ID 通常希望被删除。
考虑以下 URI 查询字符串
SID=BC3781C3-2E02-4A11-89CF-34E5CFE8B0EF&UID=44332&L=EN&M=1&H=1&UNC=0&SRC=LK&RT=62
我们希望从中删除 SID 和 UID 参数。如果您同时使用 lua-nginx-module,则很容易实现:
location = /t {
rewrite_by_lua '
local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args()
args.SID = nil
args.UID = nil
ngx.req.set_uri_args(args)
';
echo $args;
}
在这里,我们使用来自 echo-nginx-module 的 echo 指令来输出最终的 $args 值。您可以将其替换为您的 srcache-nginx-module 配置和上游配置。让我们使用 curl 测试此 /t 接口:
$ curl 'localhost:8081/t?RT=62&SID=BC3781C3-2E02-4A11-89CF-34E5CFE8B0EF&UID=44332&L=EN&M=1&H=1&UNC=0&SRC=LK'
M=1&UNC=0&RT=62&H=1&L=EN&SRC=LK
值得一提的是,如果您希望保留 URI 参数的顺序,则可以直接对 $args 的值进行字符串替换,例如,
location = /t {
rewrite_by_lua '
local args = ngx.var.args
newargs, n, err = ngx.re.gsub(args, [[\b[SU]ID=[^&]*&?]], "", "jo")
if n and n > 0 then
ngx.var.args = newargs
end
';
echo $args;
}
现在再次用原始 curl 命令测试,我们得到了正是我们所期望的结果:
RT=62&L=EN&M=1&H=1&UNC=0&SRC=LK
但出于缓存目的,规范化 URI 参数顺序是有益的,以便提高缓存命中率。而 LuaJIT 或 Lua 使用的哈希表条目顺序可以作为一个不错的副作用来规范化顺序。
指令
srcache_fetch
语法: srcache_fetch <method> <uri> <args>?
默认: 无
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 后访问
此指令注册一个访问阶段处理程序,该处理程序将发出一个 Nginx 子请求以查找缓存。
当子请求返回状态代码不是 200 时,将发出缓存未命中的信号,控制流将继续到后续阶段,包括由 ngx_http_proxy_module、 ngx_http_fastcgi_module 和其他模块配置的内容阶段。如果子请求返回 200 OK,则发出缓存命中信号,此模块将直接将子请求的响应作为当前主请求的响应发送给客户端。
此指令将始终在访问阶段的末尾运行,因此 ngx_http_access_module 的 allow 和 deny 将始终在此指令 之前 运行。
您可以使用 srcache_fetch_skip 指令选择性地禁用缓存查找。
srcache_fetch_skip
语法: srcache_fetch_skip <flag>
默认: srcache_fetch_skip 0
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 后访问
<flag> 参数支持 Nginx 变量。当此参数的值不为空 且 不等于 0 时,获取过程将被无条件跳过。
例如,要跳过具有名为 foo 的值为 bar 的 cookie 的请求,我们可以写
location / {
set $key ...;
set_by_lua $skip '
if ngx.var.cookie_foo == "bar" then
return 1
end
return 0
';
srcache_fetch_skip $skip;
srcache_store_skip $skip;
srcache_fetch GET /memc $key;
srcache_store GET /memc $key;
# proxy_pass/fastcgi_pass/content_by_lua/...
}
$skip 变量的值在(较早的)重写阶段。类似地,$key 变量也可以使用 set_by_lua 或 rewrite_by_lua 指令通过 Lua 计算。
标准的 map 指令也可以用于计算上述示例中使用的 $skip 变量的值:
map $cookie_foo $skip {
default 0;
bar 1;
}
但您的 map 语句应放入 nginx.conf 文件中的 http 配置块中。
srcache_store
语法: srcache_store <method> <uri> <args>?
默认: 无
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 输出过滤器
此指令注册一个输出过滤器处理程序,该处理程序将发出一个 Nginx 子请求,以将当前主请求的响应保存到缓存后端。子请求的状态代码将被忽略。
您可以使用 srcache_store_skip 和 srcache_store_max_size 指令在缓存未命中时禁用某些请求的缓存。
自 v0.12rc7 版本以来,响应状态行、响应头和响应体都将被放入缓存。默认情况下,以下特殊响应头将不会被缓存:
- Connection
- Keep-Alive
- Proxy-Authenticate
- Proxy-Authorization
- TE
- Trailers
- Transfer-Encoding
- Upgrade
- Set-Cookie
您可以使用 srcache_store_pass_header 和/或 srcache_store_hide_header 指令来控制缓存哪些头部,哪些不缓存。
原始响应的数据块会在到达时立即发出。 srcache_store 仅在输出过滤器中复制和收集数据,而不会推迟将其发送到下游。
但请注意,即使所有响应数据将立即发送,当前 Nginx 请求的生命周期也不会在 srcache_store 子请求完成之前结束。这意味着在服务器端关闭 TCP 连接的延迟(当 HTTP keepalive 被禁用时,但适当的 HTTP 客户端应主动关闭连接,这不会增加额外的延迟或其他问题)或在同一 TCP 连接上服务下一个请求时(当 HTTP keepalive 正在运行时)。
srcache_store_max_size
语法: srcache_store_max_size <size>
默认: srcache_store_max_size 0
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 输出头过滤器
当响应体长度超过此大小时,此模块将不会尝试使用 srcache_store 指定的子请求模板将响应体存储到缓存中。
这在使用对输入数据有严格上限的缓存存储后端时特别有用。例如,Memcached 服务器对每个项的默认限制为 1 MB。
当指定 0(默认值)时,将没有限制检查。
srcache_store_skip
语法: srcache_store_skip <flag>
默认: srcache_store_skip 0
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 输出头过滤器
<flag> 参数支持 Nginx 变量。当此参数的值不为空 且 不等于 0 时,存储过程将被无条件跳过。
自 v0.25 版本以来, <flag> 表达式(可能包含 Nginx 变量)可以被评估多达两次:第一次是在响应头被发送后,如果 <flag> 表达式没有被评估为真值,则在响应体数据流结束后再次评估。在 v0.25 之前,仅执行第一次评估。
以下是使用 Lua 设置 $nocache 的示例,以避免存储包含字符串 "/tmp" 的 URI:
set_by_lua $nocache '
if string.match(ngx.var.uri, "/tmp") then
return 1
end
return 0';
srcache_store_skip $nocache;
srcache_store_statuses
语法: srcache_store_statuses <status1> <status2> ..
默认: srcache_store_statuses 200 301 302 307 308
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 输出头过滤器
此指令根据响应状态码控制要存储到缓存的响应。
默认情况下,仅 200、301、302、307 和 308 响应将被存储到缓存,任何其他响应将跳过 srcache_store。
您可以为希望缓存的响应状态码指定任意正数,包括错误码,如 404 和 503。例如:
srcache_store_statuses 200 201 301 302 307 308 404 503;
此指令至少应给出一个参数。
此指令首次在 v0.13rc2 版本中引入。
srcache_store_ranges
语法: srcache_store_ranges on|off
默认: srcache_store_ranges off
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 输出体过滤器
当此指令开启时(默认关闭), srcache_store 还将存储由标准 ngx_http_range_filter_module 生成的 206 部分内容响应。如果您开启此指令,必须将 $http_range 添加到您的缓存键中。例如,
location / {
set $key "$uri$args$http_range";
srcache_fetch GET /memc $key;
srcache_store PUT /memc $key;
}
此指令首次在 v0.27 版本中引入。
srcache_header_buffer_size
语法: srcache_header_buffer_size <size>
默认: srcache_header_buffer_size 4k/8k
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 输出头过滤器
此指令控制序列化响应头时的头缓冲区 srcache_store。默认大小为页面大小,通常为 4k 或 8k,具体取决于特定平台。
请注意,缓冲区并不用于保存所有响应头,而只是每个单独的头。因此,缓冲区仅需足够大以容纳最长的响应头。
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
srcache_store_hide_header
语法: srcache_store_hide_header <header>
默认: 无
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 输出头过滤器
默认情况下,此模块缓存所有响应头,除了以下头:
- Connection
- Keep-Alive
- Proxy-Authenticate
- Proxy-Authorization
- TE
- Trailers
- Transfer-Encoding
- Upgrade
- Set-Cookie
您可以通过列出它们的名称(不区分大小写)来隐藏更多响应头,以便从 srcache_store 中排除它们。例如,
srcache_store_hide_header X-Foo;
srcache_store_hide_header Last-Modified;
在单个位置中允许多次出现此指令。
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
另请参见 srcache_store_pass_header。
srcache_store_pass_header
语法: srcache_store_pass_header <header>
默认: 无
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 输出头过滤器
默认情况下,此模块缓存所有响应头,除了以下头:
- Connection
- Keep-Alive
- Proxy-Authenticate
- Proxy-Authorization
- TE
- Trailers
- Transfer-Encoding
- Upgrade
- Set-Cookie
您可以通过列出它们的名称(不区分大小写)来强制 srcache_store 存储来自 srcache_store 的一个或多个响应头。例如,
srcache_store_pass_header Set-Cookie;
srcache_store_pass_header Proxy-Autenticate;
在单个位置中允许多次出现此指令。
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
另请参见 srcache_store_hide_header。
srcache_methods
语法: srcache_methods <method>...
默认: srcache_methods GET HEAD
上下文: http、server、location
阶段: 后访问、输出头过滤器
此指令指定被 srcache_fetch 或 srcache_store 考虑的 HTTP 请求方法。未列出的 HTTP 请求方法将完全跳过缓存。
允许以下 HTTP 方法:GET、HEAD、POST、PUT 和 DELETE。无论在此指令中是否存在,GET 和 HEAD 方法始终隐式包含在列表中。
请注意,自 v0.17 版本以来, HEAD 请求始终被 srcache_store 跳过,因为它们的响应从不携带响应体。
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
srcache_ignore_content_encoding
语法: srcache_ignore_content_encoding on|off
默认: srcache_ignore_content_encoding off
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 输出头过滤器
当此指令关闭时(默认开启),非空的 Content-Encoding 响应头将导致 srcache_store 跳过将整个响应存储到缓存中,并在 nginx 的 error.log 文件中发出警告,如下所示:
[warn] 12500#0: *1 srcache_store skipped due to response header "Content-Encoding: gzip"
(maybe you forgot to disable compression on the backend?)
开启此指令将忽略 Content-Encoding 响应头,并像往常一样存储响应(并且没有警告)。
建议始终通过在 nginx.conf 文件中指定以下行来禁用后端服务器的 gzip/deflate 压缩:
proxy_set_header Accept-Encoding "";
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
srcache_request_cache_control
语法: srcache_request_cache_control on|off
默认: srcache_request_cache_control off
上下文: http、server、location
阶段: 后访问、输出头过滤器
当此指令开启时,请求头 Cache-Control 和 Pragma 将被此模块以以下方式尊重:
- 当请求头
Cache-Control: no-cache和/或Pragma: no-cache存在时,将跳过 srcache_fetch,即缓存查找操作。 - 当请求头
Cache-Control: no-store被指定时,将跳过 srcache_store,即缓存存储操作。
关闭此指令将禁用此功能,并被认为对主要依赖缓存以提高速度的繁忙网站更安全。
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
另请参见 srcache_response_cache_control。
srcache_response_cache_control
语法: srcache_response_cache_control on|off
默认: srcache_response_cache_control on
上下文: http、server、location
阶段: 输出头过滤器
当此指令开启时,响应头 Cache-Control 和 Expires 将被此模块以以下方式尊重:
Cache-Control: private跳过 srcache_store,Cache-Control: no-store跳过 srcache_store,Cache-Control: no-cache跳过 srcache_store,Cache-Control: max-age=0跳过 srcache_store,- 和
Expires: <date-no-more-recently-than-now>跳过 srcache_store。
此指令优先于 srcache_store_no_store、 srcache_store_no_cache 和 srcache_store_private 指令。
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
另请参见 srcache_request_cache_control。
srcache_store_no_store
语法: srcache_store_no_store on|off
默认: srcache_store_no_store off
上下文: http、server、location
阶段: 输出头过滤器
开启此指令将强制具有 Cache-Control: no-store 头的响应在 srcache_response_cache_control 开启时存储到缓存中,前提是其他条件满足。默认值为 off。
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
srcache_store_no_cache
语法: srcache_store_no_cache on|off
默认: srcache_store_no_cache off
上下文: http、server、location
阶段: 输出头过滤器
开启此指令将强制具有 Cache-Control: no-cache 头的响应在 srcache_response_cache_control 开启时存储到缓存中,前提是其他条件满足。默认值为 off。
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
srcache_store_private
语法: srcache_store_private on|off
默认: srcache_store_private off
上下文: http、server、location
阶段: 输出头过滤器
开启此指令将强制具有 Cache-Control: private 头的响应在 srcache_response_cache_control 开启时存储到缓存中,前提是其他条件满足。默认值为 off。
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
srcache_default_expire
语法: srcache_default_expire <time>
默认: srcache_default_expire 60s
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 输出头过滤器
此指令控制在响应头中未指定 Cache-Control: max-age=N 或 Expires 时,允许的 $srcache_expire 变量值的默认过期时间。
<time> 参数值默认为秒。但最好始终明确指定时间单位以避免混淆。支持的时间单位有 "s"(秒)、"ms"(毫秒)、"y"(年)、"M"(月)、"w"(周)、"d"(天)、"h"(小时)和 "m"(分钟)。例如,
srcache_default_expire 30m; # 30 分钟
此时间必须少于 597 小时。
零过期时间的语义取决于您当前使用的实际缓存后端存储,这与此模块无关。例如,在 memcached 的情况下,零过期时间意味着该项将永远不会过期。
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
srcache_max_expire
语法: srcache_max_expire <time>
默认: srcache_max_expire 0
上下文: http、server、location、location if
阶段: 输出头过滤器
此指令控制允许的 $srcache_expire 变量值的最大过期时间。此设置优先于其他计算方法。
<time> 参数值默认为秒。但最好始终明确指定时间单位以避免混淆。支持的时间单位有 "s"(秒)、"ms"(毫秒)、"y"(年)、"M"(月)、"w"(周)、"d"(天)、"h"(小时)和 "m"(分钟)。例如,
srcache_max_expire 2h; # 2 小时
此时间必须少于 597 小时。
当指定 0 时(默认设置),则将 没有 限制。
此指令首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
变量
$srcache_expire
类型: 整数
可缓存: 否
可写: 否
此 Nginx 变量给出当前响应被存储到缓存中的推荐过期时间(以秒为单位)。计算值的算法如下:
- 当响应头
Cache-Control: max-age=N被指定时,则使用N作为过期时间, - 否则如果指定了响应头
Expires,则通过从Expires头中指定的时间减去当前时间戳来获得过期时间, - 当既未指定
Cache-Control: max-age=N也未指定Expires头时,使用 srcache_default_expire 指令中指定的值。
如果上述算法中获得的值超过最大值(如果有的话),则此变量的最终值将是由 srcache_max_expire 指令指定的值。
您不必使用此变量作为过期时间。
此变量首次在 v0.12rc7 版本中引入。
$srcache_fetch_status
类型: 字符串
可缓存: 否
可写: 否
此 Nginx 变量评估缓存系统的“获取”阶段的状态。可能的三个值为 HIT、MISS 和 BYPASS。
当“获取”子请求返回的状态码不是 200 或其响应数据不规范时,此变量评估为 MISS。
此变量的值仅在 access 请求处理阶段后有意义,或者始终给出 BYPASS。
此变量首次在 v0.14 版本中引入。
$srcache_store_status
类型: 字符串
可缓存: 否
可写: 否
此 Nginx 变量给出“存储”阶段的当前缓存状态。可以获得两个可能的值,STORE 和 BYPASS。
由于“存储”子请求的响应始终被丢弃,因此只要实际发出了“存储”子请求,此变量的值将始终为 STORE。
此变量的值至少在当前(主)请求的请求头被发送时才有意义。如果主请求未指定 Content-Length 响应头,则最终结果只能在所有响应体发送后获得。
此变量首次在 v0.14 版本中引入。
已知问题
- 在某些系统上,启用 aio 和/或 sendfile 可能会导致 srcache_store 无法正常工作。您可以在由 srcache_store 配置的 locations 中禁用它们。
- srcache_store 指令无法用于捕获由 echo-nginx-module 的子请求指令(如 echo_subrequest_async 和 echo_location)生成的响应。建议使用 HttpLuaModule 来发起和捕获子请求,这应该可以与 srcache_store 一起使用。
注意事项
- 建议禁用后端服务器的 gzip 压缩,并使用 nginx 的 ngx_http_gzip_module 来完成此工作。在使用 ngx_http_proxy_module 的情况下,您可以使用以下配置设置禁用后端 gzip 压缩:
proxy_set_header Accept-Encoding ""; - 不要在与此模块相同的位置中使用 ngx_http_rewrite_module 的 if 指令,因为 “if 是邪恶的”。相反,使用 ngx_http_map_module 或 lua-nginx-module 结合此模块的 srcache_store_skip 和/或 srcache_fetch_skip 指令。例如:
map $request_method $skip_fetch { default 0; POST 1; PUT 1; } server { listen 8080; location /api/ { set $key "$uri?$args"; srcache_fetch GET /memc $key; srcache_store PUT /memc $key; srcache_methods GET PUT POST; srcache_fetch_skip $skip_fetch; # proxy_pass/drizzle_pass/content_by_lua/echo/... } }
故障排除
要调试问题,您应始终首先检查 Nginx 的 error.log 文件。如果没有打印错误消息,则需要启用 Nginx 调试日志以获取更多详细信息,如 调试日志 中所述。
一些初学者常见的陷阱:
- 原始响应携带一个明确禁用缓存的
Cache-Control头,而您没有配置像 srcache_response_cache_control 这样的指令。 - 原始响应已经经过 gzip 压缩,默认情况下不会被缓存(请参见 srcache_ignore_content_encoding)。
- 当使用过长的键时,Memcached 可能会返回
CLIENT_ERROR bad command line format(截至版本 1.4.25,键长度为 250 个字符)。因此,使用set_md5 $key $uri$args;而不是set $key $uri$args;更安全。set_md5指令(及更多)可从 OpenResty 的 set-misc 模块 获取。 - 当尝试将大于 1m 的对象存储到存储后端时,Nginx 可能会返回
client intended to send too large body,在这种情况下,必须将 nginx 的client_max_body_size设置为更高的值。 - Memcached 可能无法存储大于 1m 的对象,导致错误,如
srcache_store subrequest failed status=502。自版本 1.4.2 起,memcached 支持命令行-I选项以覆盖每个 slab 页的默认大小。有关更多信息,请阅读其手册页。
测试套件
此模块附带一个 Perl 驱动的测试套件。 测试用例 也是 声明式的。感谢 Perl 领域的 Test::Nginx 模块。
要在您这边运行它:
$ PATH=/path/to/your/nginx-with-srcache-module:$PATH prove -r t
由于所有测试脚本(.t 文件)都使用单个 nginx 服务器(默认情况下为 localhost:1984),因此在调用 prove 工具时指定 -jN 并行运行测试套件是没有意义的。
测试套件的某些部分还需要启用 ngx_http_rewrite_module、 echo-nginx-module、 rds-json-nginx-module 和 drizzle-nginx-module 模块。
另见
GitHub
您可以在 nginx-module-srcache 的 GitHub 仓库 中找到此模块的其他配置提示和文档。